Understanding Sample Rate, Bit Rate And Bit Depth
By Alireza Alavi • 6 minutes read •
Table of Contents
- Our World Is Continuous (Analog)
- What Are Digital Signals?
- How To Convert Analog Signal To Digital Signal
- Why Is It Called "bit depth"?
- What Is "bit rate"?
- Relevant And Good Posts
- Sources
These are my notes as a software engineer on understanding Sample rate, bit rate and bit depth.
The explanations might seem incoherent at first, but I think if you read the whole post it becomes more clear. Also read the relevant and good posts for some other explanations from other perspectives.
The notes are written in an outline style.
Our World Is Continuous (Analog)
-
Sounds in our world are analog. The sounds that you hear or the sounds that you make are all analog signals
-
Analog signals happen in continuous time. meaning, if we want to draw a diagram of the signal representing it's intensity on one axis and time on another (A signal is a series of changes in time), the diagram would look like this:
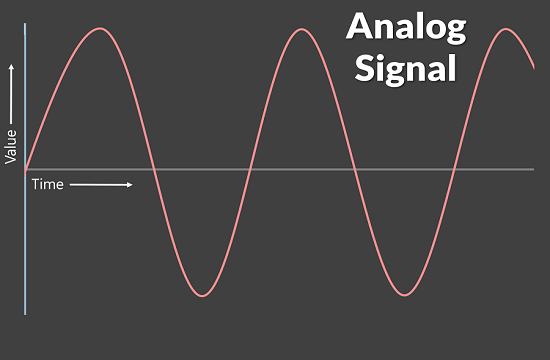
-
In order for these signals to be understood, used and processed in our digital devices (phones, PC, TV, etc.) they should be converted into digital signals, used within the device and then either be sent to another digital medium, or be converted to an analog signal again and then sent to an analog medium (Digital signals are explained later).
-
Example from sound:
Your voice(analog) -> travels through air to reach microphone(analog) -> microphone vibrates (analog) -> gets converted to digital -> sent as digital signal to a speaker via a digital medium (digital signals on a wire)-> the speaker vibrates the air in a way that recreates your voice (analog) -> travels through air (analog) -> The listener's ear picks up the vibrations(analog) -> Signals in nervous system (?)
Time, As we define it, is continuous(or as continuous as it gets) so anything happening in our world is continuous, since it happens in time.
Also note that all of the things that I said might not be true, since we really don't have a concrete definition of what time is, and the line between continuity and being discrete is blurry(like most other things in our world).
What Are Digital Signals?
- A digital signal is a type of discrete signal(as opposed to continuous ).
- Discrete signal: we will ignore the continuity of time, and assume that time happens in discrete amounts. So there will be nothing there between time 1 and time 2.
- Now digital means: our time is discrete, and our intensities are also discrete
-
In digital signal processing,
a digital signal is a representation of a physical(analog) signal that is
sampled and quantized. A digital signal is an abstraction that is
discrete in time and amplitude. [1]
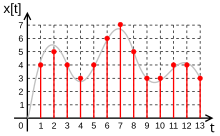
See how in the above diagram, no values can exist between the defined values.
How To Convert Analog Signal To Digital Signal
- Now, With that explanation of digital signals, we can understand the basics of how we convert analog signal to digital:
- In discrete time intervals (for example every second), we will sample our signal. Meaning, we will measure it at that moment. This is called our sample rate (here our sample rate is 1 sample per second)
- Now that we took the sample, since our original signal is continuous, our measured intensity value is a Real number($\mathbb{R}$) and can be something like 0.333333.... or $\pi$ (3.14...), we cannot use that number in our digital system! So we have to round it to a defined value.
- Imagine our digital signal graph as a checkered graph. The vertical lines are your time intervals (sample rate as we defined earlier) and the vertical lines are your defined values, to which you will round your intensities. The more dense the vertical lines are, the higher your sample rate. And the more dense your horizontal lines, the higher accuracy for rounding your intensities you have (Bit depth)
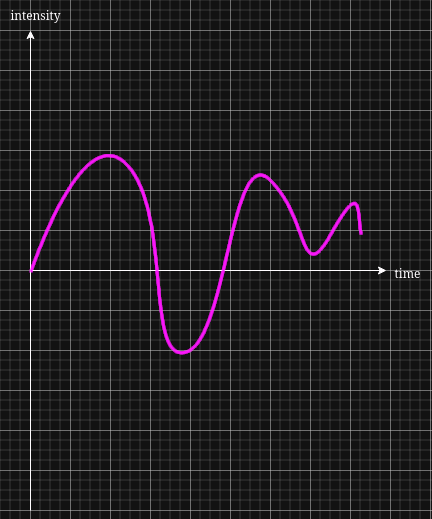
- Analog signal:
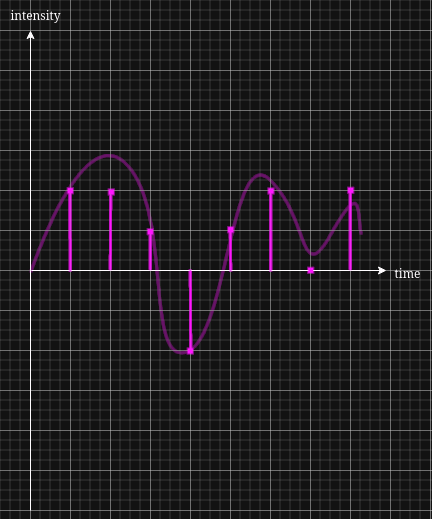
- Digital signal with lower bit depth and sample rate ( we consider the thicker lines as our bit depth and sample rate values in this example ):
- Digital signal with higher bit depth and sample rate ( all lines are considered as our bit depth and sample rate values):
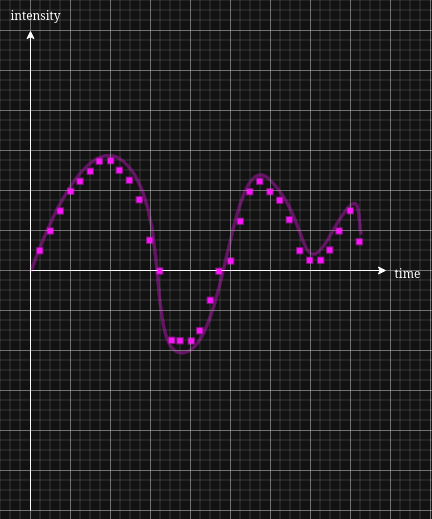
- Notice how as we raise the sample rate and bit depth, we get closer to our actual analog signal


Why Is It Called "bit depth"?
-
A "bit" is the smallest value in a digital system. it's either 0 or 1
-
One bit can represent 2 values, and 2 bits can represent 4 values. The general rule is with $n$ bits we can represent $2^n$ values.
-
Bit depth refers to "how many bits do we have for the number we want to represent our intensity with?" so the more bits we have, more values we can express. so our estimations of our analog signal's intensity becomes more accurate
-
A 24-bit audio is more accurate in terms of the intensity of each sample than a 16-bit
-
Example with color: An image with 8-bit depth is more accurate in displaying different intensities (shades) of colors

We can say that:
if (sample_rate $\rightarrow \infty$ and bit_depth $\rightarrow \infty$) then Our signal is analog
What Is "bit rate"?
-
bit rate (bitrate or as a variable R) is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time.[2]
-
The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction with an SI prefix such as kilo (1 kbit/s = 1,000 bit/s), mega (1 Mbit/s = 1,000 kbit/s), giga (1 Gbit/s = 1,000 Mbit/s) or tera (1 Tbit/s = 1,000 Gbit/s).[2]
Relevant And Good Posts
- Let's learn about waveforms - The pudding
- Bit rate vs. Sample rate vs. Bit depth - waveroom
- Continuous vs discrete signals. What is the difference? - engineeryoursound
- Digital audio basics: sample rate and bit depth - izotope